Hemorrhoid bleeding can lead to harmful effects, particularly iron deficiency anemia if the blood loss is significant. Blood in a hemorrhoid may clot, causing tissue around it to die from blood clots. Hemorrhoids can cause chronic anemia if left untreated. Anemia caused by hemorrhoids should be treated medically.
Anemia caused by ongoing blood loss from hemorrhoids can be rare. Anemia is caused by insufficient healthy red blood cells throughout the body.
This blog post discusses hemorrhoid bleeding and anemia, symptoms of hemorrhoid bleeding anemia, diagnosis of hemorrhoids and anemia, and ways to prevent hemorrhoids and anemia.
Hemorrhoid Bleeding Anemia: 6 Symptoms

The severity of hemorrhoid bleeding-induced anemia depends on the amount of blood lost. Some common symptoms include
Fatigue
Anemia which results from hemorrhoid bleeding and can cause chronic fatigue. The body cannot produce enough red blood cells, which carry oxygen throughout the body, resulting in fatigue. Acute fatigue can interfere with everyday activities like walking, standing, and breathing.
Weakness
Weakness can also be caused by anemia, a condition caused by hemorrhoid bleeding. Oxygen deprivation can cause muscles to weaken, making it difficult to perform physical tasks. The result can be decreased quality of life and well-being.
Irritability
Anemia due to hemorrhoid bleeding can cause mood swings, irritability, and emotional instability. Anxiety, depression, and agitation are caused by a lack of oxygen in the brain.
Dizziness
Dizziness or lightheadedness can result from hemorrhoids when there is insufficient oxygen in the brain, and blood flow decreases, causing dizzy spells or fainting. Stand up slowly and be careful when driving or operating machinery to avoid dizziness caused by anemia.
Pale Skin
Anemia resulting from hemorrhoid bleeding can cause pale skin. Red blood cells are needed to make hemoglobin, which gives skin its natural color. As a result, those with anemia often appear pale or even yellowish.
Cold Extremities
Anemia from hemorrhoid bleeding can cause icy hands and feet. This is because of limited blood flow as the body tries to conserve its little oxygen. In extreme cases, anemia can lead to frostbite-like symptoms, such as numbness, tingling, and even tissue damage. Symptoms like these require immediate medical attention.
4 Diagnosis for Hemorrhoid Bleeding and Anemia
Hemorrhoid bleeding and anemia can be a debilitating health condition that could lead to severe health complications if left untreated. Therefore, it is crucial to manage this condition effectively and efficiently. There are various ways to manage hemorrhoid bleeding and anemia effectively. Here are some effective methods of managing hemorrhoid bleeding and anemia:
Blood tests
A complete blood count (CBC) can show decreased hemoglobin and hematocrit levels, indicative of anemia. The serum ferritin test can also diagnose iron deficiency anemia.
Colonoscopy
A visual examination of the colon can help identify any sources of bleeding, such as hemorrhoids or polyps.
Endoscopy
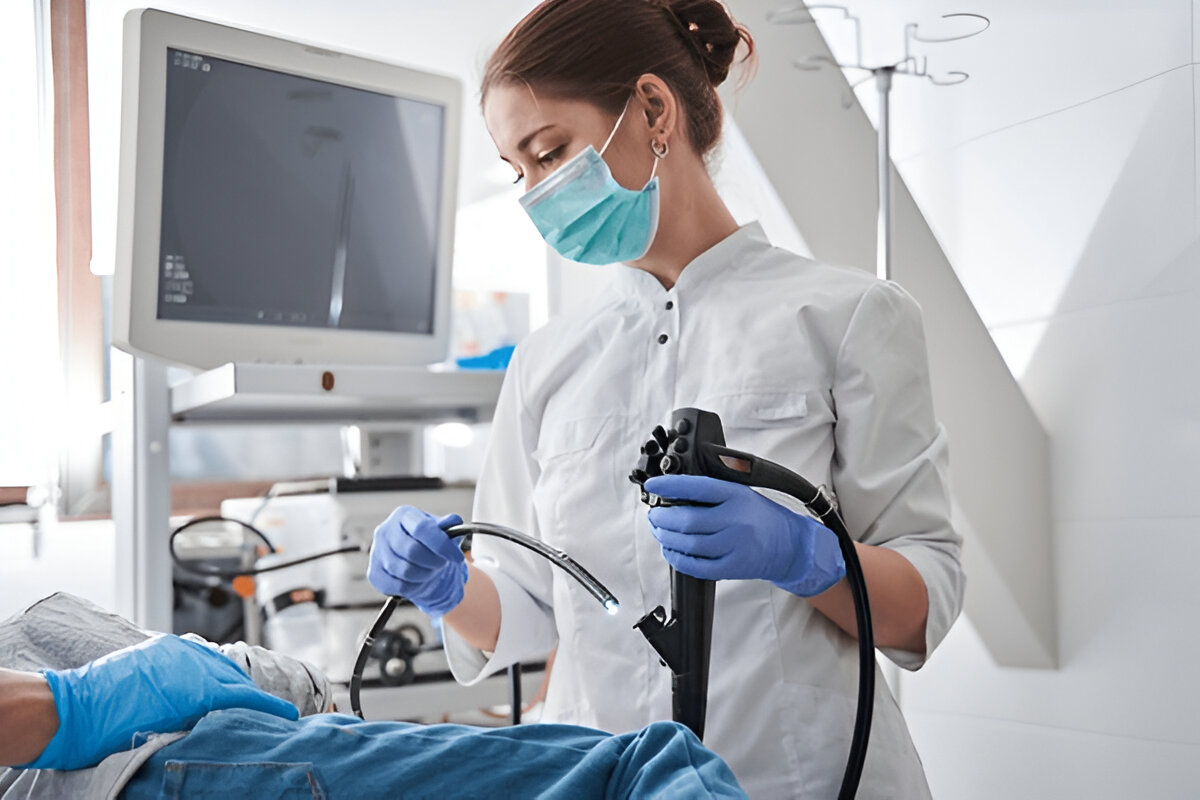

Upper gastrointestinal tract examinations are performed with a flexible tube and a camera.
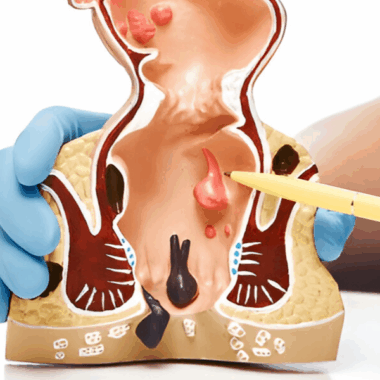
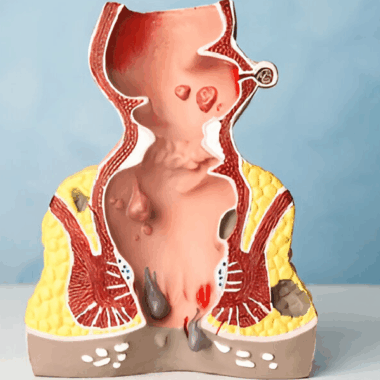
A hemorrhoid bleeding-induced anemia can show a more dangerous condition, for example, colorectal cancer or inflammatory bowel disease. Hemorrhoid bleeding anemia is diagnosed through diagnostic tests, a medical history, and a physical examination.
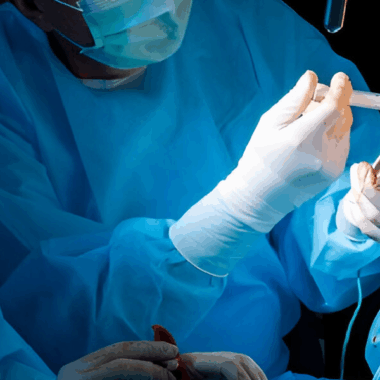
Anemia and Bleeding Hemorrhoids: 6 Surgical Options
Where hemorrhoids are chronic and severe, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgical options for treating hemorrhoids include rubber band ligation, sclerotherapy, and hemorrhoidectomy.
Hemorrhoidectomy
Surgery to remove hemorrhoidal tissue is performed only if other treatments have failed. There is a longer recovery time and a higher risk of complications, such as pain, bleeding, and narrowing of the rectus.
Rubber Band Ligation
A rubber band is wrapped around a hemorrhoid's base, cutting off its blood supply. Within a week, the hemorrhoid shrinks and falls off. It is a safe and effective treatment with a low risk of complications.
Sclerotherapy
Hemorrhoids are shrunk by injecting a solution directly into them. Although less invasive than hemorrhoidectomy, it requires multiple treatments.
Laser Therapy
This technique uses a laser to vaporize the hemorrhoid, eliminating it. Although more effective than a hemorrhoidectomy, it may not be suitable for larger hemorrhoids.
Infrared Coagulation
The hemorrhoids shrink and eventually fall off because infrared light coagulates the blood vessels that supply them. Infrared coagulation is a quick and painless procedure that can be done in a doctor's office.
Hemorrhoids less severe than those with large or prolapsed hemorrhoids may benefit from this procedure.
Stapled Hemorrhoidectomy

Staple placement is a surgical procedure that stops blood flow to hemorrhoids. This method reduces recovery time when treating severe hemorrhoids compared to traditional surgery.
Anemia and bleeding hemorrhoids can be treated surgically, but recovery time varies.
Rubber band ligation has low risks and is safe and effective. Sclerotherapy or laser therapy may be less invasive, but multiple treatments may be needed. To determine the best treatment option, consult a healthcare professional.
Hemorrhoids and Anemia: 7 Prevention
Because of hemorrhoids, red blood cells cannot carry oxygen throughout the body. To prevent these health problems, here are some tips you can follow:
- Increase daily water intake: Drink up to eight glasses of water daily to soften stools and ease the discomfort of hemorrhoids during bowel movements.
- Eat a fiber-rich diet: Fiber-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains prevent constipation and maintain regular stools.
- Exercise regularly: Exercise helps circulate blood and prevent constipation, reducing the risk of hemorrhoids.
- Avoid sitting for long periods: Long periods of sitting on hard surfaces may increase pressure on the rectum and anus, resulting in hemorrhoids. Standing up or walking around every hour or two if you have a sitting job is recommended.
- Avoid lifting heavy objects: Lifting heavy objects can increase intra-abdominal pressure, leading to hemorrhoids and bleeding.
- Use proper toileting techniques: Avoid pushing and straining when using the restroom, which can cause hemorrhoids to bleed. Instead, sit on the toilet seat for 10 minutes and try not to force the stools out.
- Manage stress levels: High stress levels can increase the risk of constipation, leading to hemorrhoid bleeding. You can manage stress with deep breathing, meditation, yoga, or massage. Yoga or massage can help.
Conclusion
Anemia and hemorrhoids are two common health conditions associated with negative health outcomes. Avoid serious complications by immediately identifying the underlying cause and seeking medical attention. Surgery is usually unnecessary if lifestyle changes and medications are implemented.
Diagnosing and treating hemorrhoid bleeding or anemia requires the help of a healthcare provider. Remember, taking care of your health is a good use of time, so stay informed and healthy.
FAQs
There is a risk of developing anemia from hemorrhoid bleeding for some people. Many factors contribute to anemia from hemorrhoid bleeding, such as frequent bleeding, prolonged bleeding, liver disease, and a poor diet lacking iron and other essential nutrients.
Anemia caused by hemorrhoid bleeding may be treated with medication alone. Supplements containing iron replenish iron stores in the body and promote red blood cell production. If bleeding persists or is severe, other treatments, such as surgery to remove hemorrhoids or cauterization, may be needed.
Hemorrhoids bleeding and anemia are not always treated with surgery to prevent further bleeding or to control anemia. Less invasive treatments, such as stool softeners, fiber supplements, and sitz baths, can reduce hemorrhoid symptoms and prevent further bleeding. A surgical procedure may be necessary if the bleeding is severe or recurrent to remove the hemorrhoids or treat the underlying cause.