Hemorrhoids are swellings in the rectum or anus, causing discomfort but usually not life-threatening. Bowel cancer can be deadly and may present symptoms like weight loss and changes in bowel habits. Understanding the differences between the two is essential to seek appropriate medical attention.
The symptoms of hemorrhoids are often complex, sore lumps, while colon cancer can cause diarrhea, constipation, and weight loss.
In this blog post, we'll discuss the disparities between the causes and factors of hemorrhoid and cancer, diagnostic methods for detecting them, risks and complications associated with each, and treatment options available.
Hemorrhoid VS Cancer: 5 Major Difference

Hemorrhoids and cancer are distinct conditions that can affect people differently. Although they may have shared symptoms like pain and discomfort, they differ in cause, prognosis, and treatment options.
Definition and Symptoms
Hemorrhoids, also known as piles, are joint swellings that occur in the anal veins, causing discomfort, itching, and bleeding. Cancer of the colon (CRC) is a complex disease that causes uncontrolled cell proliferation, leading to tumor formation in the colon, anus, or rectum. Recognizing the signs and symptoms for early detection and timely intervention is crucial.
Definition of Hemorrhoids
The hemorrhoids, which are also known as piles, are swellings in the arteries. They are a common condition and can be caused by various factors, such as constipation, straining during bowel movements, pregnancy, or prolonged periods of sitting.
Symptoms
These swellings can occur both externally and internally in the rectum. When hemorrhoids occur externally, they can cause discomfort, itching, and bleeding. Internal hemorrhoids are often painless but may still result in bleeding during bowel movements.
Hemorrhoids, although bothersome, are usually not a severe medical condition. Treatment and evaluation by a doctor is advisable if symptoms persist or worsen.
Definition of Cancer
It is a complex disease that occurs when the body's cells undergo uncontrolled proliferation, leading to the formation of tumors. One of the prevalent types is colorectal cancer (CRC), which primarily affects the colon, anus, or rectum. It typically starts an abnormal growth in the colon's lining, progressively establishing its presence and potentially spreading to other organs and tissues.
Symptoms
Early detection and timely intervention of colorectal cancer depend on recognizing the signs and symptoms. Some common indications to be mindful of include rectal bleeding, persistent abdominal pain, noticeable bowel changes, and symptoms of weakness and fatigue. They can take steps toward their health and seek medical attention by staying vigilant.
Factors that Cause Hemorrhoids and Cancer
Hemorrhoids and cancer are two health issues that affect the rectal area, but they are not the same. Hemorrhoids are a common condition that can be treated with lifestyle changes and medication; cancer is a severe disease that requires immediate medical attention. Hemorrhoids and cancer cause risk factors and symptoms. By understanding these differences, you can identify the condition you are experiencing and seek appropriate medical care.
Causes and Factors of Hemorrhoids
A hemorrhoid is a swollen vein in the rectal area that can cause itching, pain, and bleeding. Some factors that increase the risk of developing hemorrhoids include:
- Straining during bowel movements.
- Sitting for long periods.
- Obesity.
- Pregnancy.
- Chronic constipation or diarrhea.
- Aging.
Causes of Colorectal Cancer
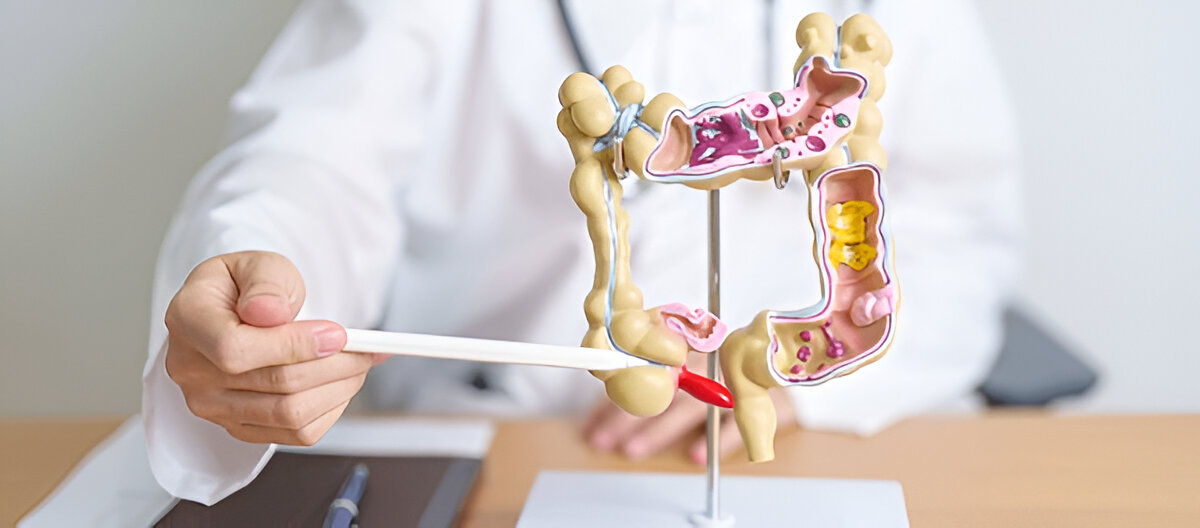
Causes of Colorectal Cancer The rectum or colon is affected by colorectal cancer. It is unknown what causes colorectal cancer. Still, it is believed to originate because of genetic mutations that cause cells in the colon or rectum to grow and divide uncontrollably. Some risk factors that may increase the risk of colorectal cancer include:
- The most common age group for this disease is people over 50.
- A family history of polyps or colorectal cancer.
- The presence of an inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis).
- Genetic mutations (such as Lynch syndrome or familial adenomatous polyposis).
Comparison of Diagnostic Methods for Hemorrhoids and Cancer
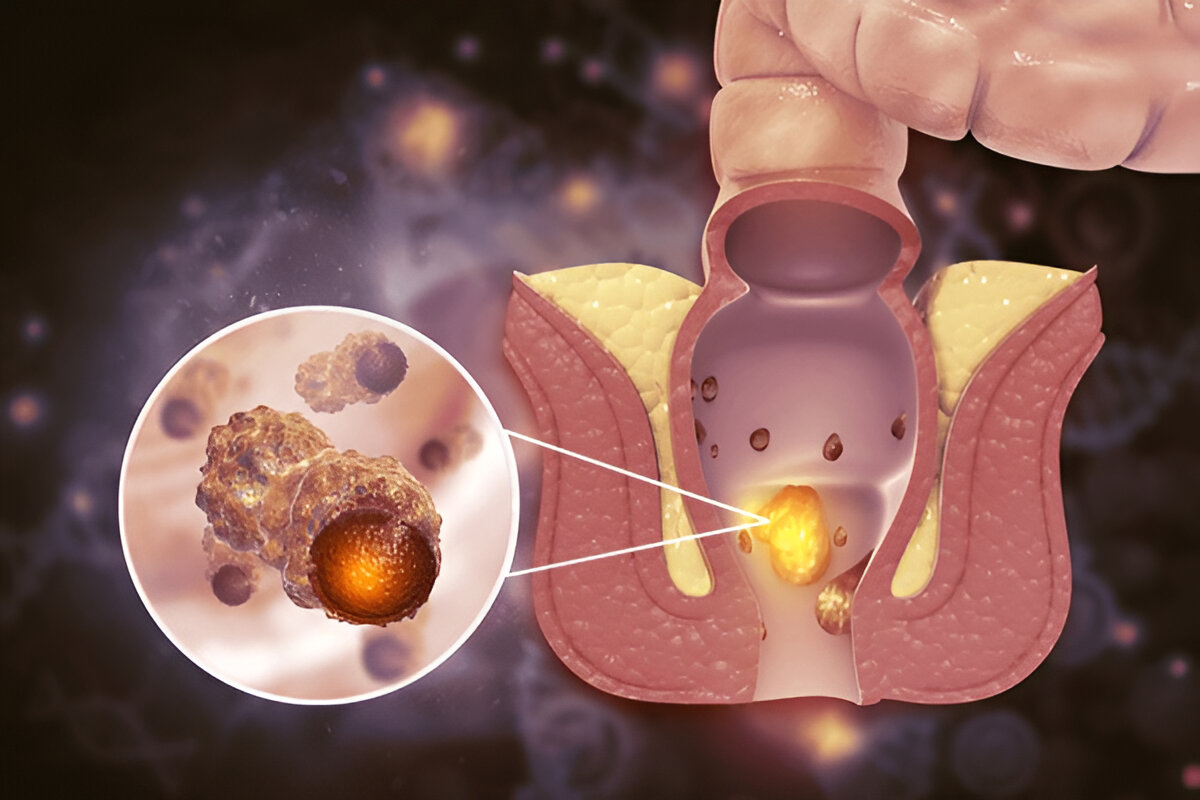
For rectal bleeding, a common concern is whether it's caused by hemorrhoids or cancer. Although both conditions can cause bleeding, they have distinct differences. Doctors use diagnostic methods to determine the cause and differentiate between hemorrhoids and cancer accurately. Here are standard diagnostic procedures for this purpose:
Diagnosing Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids are a common condition affecting millions worldwide. A variety of symptoms can be experienced, ranging from mild discomfort to severe pain. Several diagnostic methods are used to detect hemorrhoids, including:
- Physical Examination: During a physical exam, your doctor may examine your anus and rectum to look for signs of hemorrhoids, such as swelling or inflammation.
- Digital Rectal Exam (DRE): A DRE is a procedure that involves the insertion of gloved, lubricated fingers into the rectum to feel for abnormalities or masses.
- Anoscopy: You use a short, flexible tube with a light and lens on the end to examine the inside of the anus and rectum. This can help identify any hemorrhoids up close.
- Colonoscopy: Inserting a long, flexible tube with a camera on the end of the rectum and colon to look for abnormalities. This can help doctors identify any hemorrhoids and other health issues.
Diagnosing Cancer
Cancer of the rectum and anus can have similar symptoms to hemorrhoids, making diagnosis more challenging. Several diagnostic methods can help differentiate between the two, including:
- Physical Examination: A doctor may examine the anus and rectum for signs of cancer, such as a lump or mass.
- Biopsy: You take a tiny piece of tissue from the rectum or anus for examination under the microscope.
- Imaging Tests: Imaging tests such as CT scans, MRIs, or ultrasound can help detect abnormal growths or masses in the rectum or anus.
The Risks and Complications of Hemorrhoids vs Cancer
Hemorrhoids and cancer are different medical conditions, but they often cause similar symptoms, such as rectal bleeding and discomfort. Comprehending the risks and complications associated with these two conditions is crucial to plan for appropriate medical care. Here are some risks and complications of hemorrhoids and cancer.
Complications and Risks of Hemorrhoids
A hemorrhoid is a swollen blood vessel that causes pain, itching, and bleeding in the lower rectum or anus. The following are some risks and complications associated with hemorrhoids:
- Chronic Pain and Discomfort: Hemorrhoids can cause chronic pain and discomfort, particularly during bowel movements, affecting daily life.
- Anemia Due to Blood Loss: If hemorrhoids bleed frequently, they can lead to anemia, which is a condition where people lack red blood cells that carry oxygen. Anemia can cause fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath.
- Strangulation of the Hemorrhoid: In rare cases, hemorrhoids can become constricted or strangulated, cutting off blood flow to the tissue. This condition requires immediate medical attention.
- Thrombosis: Hemorrhoids, also known as piles, cause swollen blood vessels in the abdomen that can cause discomfort and pain. These swollen blood vessels can develop blood clots sometimes, leading to even more severe pain and swelling.
The Risks and Complications of Cancer
Cancer is a painful and life-threatening condition that can develop anywhere in the body. The following risks and complications are associated with cancer:
- Metastasis and Spread: Cancer cells can spread to different body parts and cause tumors in other organs, called metastasis. This can make cancer treatment more challenging and lower the chances of survival.
- Treatment Side Effects: Cancer treatment options, such as chemotherapy and radiation, can have side effects, including fatigue, nausea, hair loss, and skin irritation.
- Increased Risk of Mortality: Cancer is a leading cause of death globally. Some types of cancer have a higher mortality rate than others, depending on the cancer stage at diagnosis and the patient's overall health.
- Obstruction: The tumor can grow big enough to block the colon, leading to constipation and other gastrointestinal problems.
- Fecal Incontinence or Urgency: Chronic diarrhea from rectal cancer or surgery may cause fecal incontinence or urgency.
- Radiation Therapy Complications: Radiation therapy used to treat rectal and anal cancer may cause various complications, such as skin irritation, fatigue, and sexual dysfunction.
- Ostomy: sometimes, surgery to remove a cancer of the rectum or anus may involve creating an opening in the abdomen, called an ostomy, to eliminate stool. This can lead to complications such as skin irritation, infections, and difficulty adjusting to an alternative lifestyle.
Treatment Options Comparison for Hemorrhoids and Cancer

Cancer and hemorrhoids affect different body parts. Hemorrhoids involve swollen rectal and anal veins, while cancer denotes uncontrolled cell growth in any body part. Despite their differences, there are similarities in their treatment options. Let's compare hemorrhoid and cancer treatments.
Conservative Treatment for Hemorrhoids
Many times, hemorrhoids can be treated with traditional measures before surgery. These may include:
- Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a healthy diet, drinking plenty of fluids, increasing physical activity, and avoiding straining during bowel movements.
- Medications: Some over-the-counter creams, ointments, and suppositories can help ease pain and swelling associated with hemorrhoids. Relax is a laxative that can relieve constipation, one of the leading causes of hemorrhoids. Surgical procedures for hemorrhoids.
Surgical Procedures for Hemorrhoids
When conservative measures are ineffective, surgery may be required to remove the hemorrhoids. Some surgical procedures that may be used include:
- Rubber Band Ligation: This involves applying a small rubber band to the base of hemorrhoids, thereby preventing the bleeding and causing them to fall off.
- Hemorrhoidectomy: A surgical procedure that removes hemorrhoids with a scalpel or laser. This is usually reserved for severe hemorrhoids that do not respond to other treatment options.
Treatments for Cancer
Cancer treatments differ depending on the type and stage of cancer and the general health of the patient. Some common treatments include:
- Surgery: Removing the cancerous tumor from the body. Surgery is typically the first-line treatment for most types of cancer.
- Radiation Therapy: This involves the application of high-energy radiation in order to destroy cancer cells. Radiation may be used alone or in combination with other treatments.
- Chemotherapy: A treatment that kills cancer cells by using drugs. Chemotherapy can be combined with other treatments or used alone. It is typically used for advanced or metastatic cancer.
Conclusion
Hemorrhoids and cancer may have similar symptoms but different situations. While hemorrhoids can cause significant discomfort and physical problems in the rectal area, they are usually harmless and can be treated with medication. Cancer is more concerning and can lead to severe complications, including death, if not diagnosed and treated promptly.
It's crucial to seek medical attention if you have noticed any unusual symptoms in your rectal area and to undergo regular screening for colorectal cancer for early detection. Remember, your health is your most important asset, so take care of yourself.
FAQs
Hemorrhoids, though not directly linked to cancer, can obscure cancer symptoms through bleeding or discomfort. It is essential to be aware of this possibility and seek proper medical evaluation if such symptoms persist or worsen.
Symptoms like rectal bleeding or lumps in the anus can be caused by hemorrhoids or colon or anal cancer. Physical exams, colonoscopies, stool tests, and biopsy can help doctors tell them apart.

![Hemorrhoid vs Cancer: 5 Differences [Total]](https://jillm.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/Two-types-of-hemorrhoids-banding-anesthetics-factors-to-consider-380x380.webp)
![Hemorrhoid vs Cancer: 5 Differences [Total]](https://jillm.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/discussion-of-7-major-symptoms-of-prolapsed-hemorrhoids-380x380.png)
![Hemorrhoid vs Cancer: 5 Differences [Total]](https://jillm.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/6-Benefits-3-Use-Methods-of-Essential-Oils-for-Hemorrhoids-380x380.png)
![Hemorrhoid vs Cancer: 5 Differences [Total]](https://jillm.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Differences-Between-a-Hemorrhoid-and-a-Fissure-380x380.png)
![Hemorrhoid vs Cancer: 5 Differences [Total]](https://jillm.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/4-Precautions-5-Effects-of-Hemorrhoid-Cream-For-Skin-Tightening-380x380.png)
![Hemorrhoid vs Cancer: 5 Differences [Total]](https://jillm.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Timeframe-for-Hemorrhoid-Suppositories-Factors-Timeframe-6-Tips-380x380.png)
![Hemorrhoid vs Cancer: 5 Differences [Total]](https://jillm.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Bleeding-from-the-hemorrhoids-and-anemia-380x380.png)