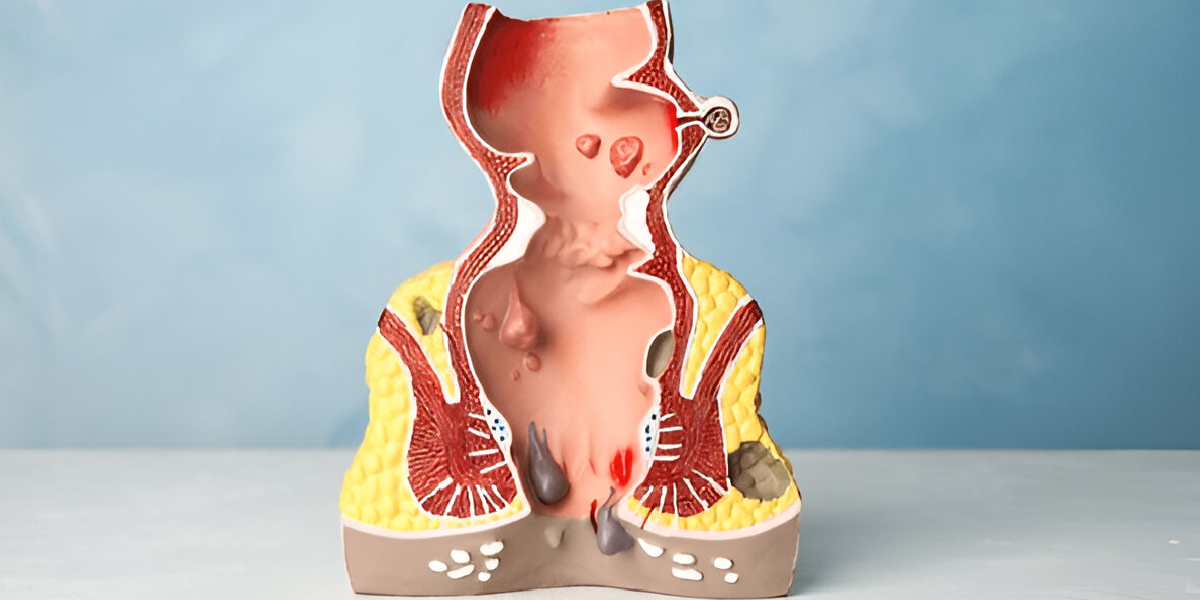
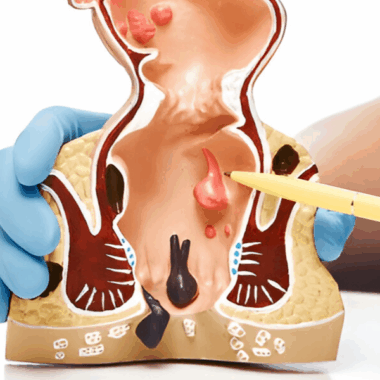
Hemorrhoids are presumed to be caused by repeated anal and rectal veins pressure. Anal fissures are caused by trauma to the anal canal, usually during bowel movements. Anal fissures are also sometimes caused by inflammatory bowel disease or infection.
Both hemorrhoids and fissures can cause discomfort, but they are very different. A proper diagnosis and timely treatment depend on understanding the differences in their causes, symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options.
In this blog post, we will explore the differences between Hemorrhoids and Fissures and provide insight on how to prevent and treat them effectively.
Hemorrhoid vs Fissure: 6 Differences
While these two conditions share some similarities, they are different in terms of their causes, symptoms, risk factors, diagnostic processes, and treatments. To help you navigate and understand these differences, this blog post will break down each aspect and compare them for convenience.
Causes
Hemorrhoids:
- Constipation, straining during bowel movements, and pressure on the veins in the rectum and anus.
- Pregnancy, obesity, aging, and a sedentary lifestyle.
Issues:
- Trauma or injury to the anus or rectum, such as during childbirth, surgery, or anal sex.
- Chronic constipation, diarrhea, or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Comparing:
Hemorrhoids are mainly caused by pressure on the veins of the anus and rectum, while fissures are primarily caused by anus or rectum trauma.
Both hemorrhoids and cracks can be worsened by constipation and straining during bowel movements.
Symptoms
Hemorrhoids:
- Painless or painful bleeding during bowel movements.
- Itching, swelling, and discomfort around the anus.
- Prolapse or protrusion of the hemorrhoids outside the anus.
Fissures:
- Sharp or burning pain during bowel movements or after, lasting several hours.
- Bleeding or spotting, especially on toilet paper.
- Itching and discomfort around the anus.
Variations between hemorrhoids and fissures:
- Hemorrhoids can cause prolapse or protrusion, while fissures do not.
- Hemorrhoids can be painless or painful, while fissures are usually painful.
- Fissures and hemorrhoids can both cause bleeding, itching, and discomfort.
Risk
Hemorrhoids:
- Aging, pregnancy, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle.
- Chronic constipation, diarrhea, and pelvic floor dysfunction.
Fissures:
- The anus or rectum is injured or traumatized.
- Chronic constipation, diarrhea, IBD, and previous anal surgery or radiation therapy.
Comparison:
- Hemorrhoids are more commonly associated with aging, pregnancy, and obesity, while fissures are associated with trauma or injury.
- Both hemorrhoids and fissures can be worsened by chronic constipation and diarrhea.
Diagnosed

Hemorrhoids:
- Physical examination of the anus and rectum, including a digital rectal exam and an anoscopy or proctoscopy.
- Stool tests and colonoscopy may be recommended to rule out other conditions.
Fissures:
- An examination of the anus and rectum, including a digital rectal exam and anoscopy or proctoscopy.
- Sometimes, an anal manometry or defecography may be recommended to assess the function of the anal sphincter or pelvic floor.
Comparison:
- Both hemorrhoids and fissures are typically diagnosed through physical examination and imaging tests.
- Colonoscopy may be more frequently recommended for hemorrhoids, while anal manometry can be used for fissures
Treatment
Hemorrhoids:
- Lifestyle changes, such as increasing fiber intake, drinking more fluids, and exercising more.
- Topical creams, ointments, and suppositories to relieve itching, swelling, and pain.
- Rubber band ligation or sclerotherapy to shrink the hemorrhoids.
- Hemorrhoidectomy or stapled hemorrhoidopexy to remove the hemorrhoids.
Fissures:
- Topical creams, ointments, and nitroglycerin to relax the anal sphincter and promote healing.
- Botulinum toxin injection to paralyze the anal sphincter and reduce pain.
- Lateral internal sphincterotomy or anal advancement flap relieves muscle spasms and fissures.
Effectiveness of Treatments and Comparison:
- Some treatments for hemorrhoids, such as lifestyle changes and rubber band ligation, may have a higher success rate than others, such as surgery.
- The success rate of treatments for fissures may vary depending on the severity and duration of the fissure, as well as the underlying cause.
Conclusion
Hemorrhoids and fissures are two distinct conditions that can cause discomfort and pain in the anal area. Although they share some similarities, understanding their differences is vital in getting the appropriate diagnosis and treatment.
By identifying the underlying causes, symptoms, and risk factors, individuals can take preventive measures and seek treatment early, leading to improved quality of life. It is important to remember that seeking medical advice and attention for any symptoms in the anal area is critical for proper diagnosis and treatment.
FAQs
The main difference between anal fissures and hemorrhoids is that anal fissures tend only to show symptoms during bowel movements, while hemorrhoids tend to cause pain all day long. The symptom difference usually indicates what the patient may suffer from without an examination.
Anal fissures and hemorrhoids can occur separately or together. Self-diagnosing sufferers often confuse these two conditions due to their similar symptoms.
Anal fissures can make pooping very painful. You may experience constipation (fewer bowel movements than usual) due to the pain. They can also cause bleeding from your anus.
The conditions can be uncomfortable and sometimes cause pain and bleeding, but they are rarely serious. Surgery may be required in severe cases, but most cases can be treated through lifestyle changes and over-the-counter medication. It is essential to consult a healthcare professional if symptoms persist or worsen.
You can prevent hemorrhoids by increasing fiber in your diet, drinking plenty of water, and exercising regularly. Avoid constipation by following the same dietary and lifestyle recommendations and using stool softeners if necessary to prevent fissures.